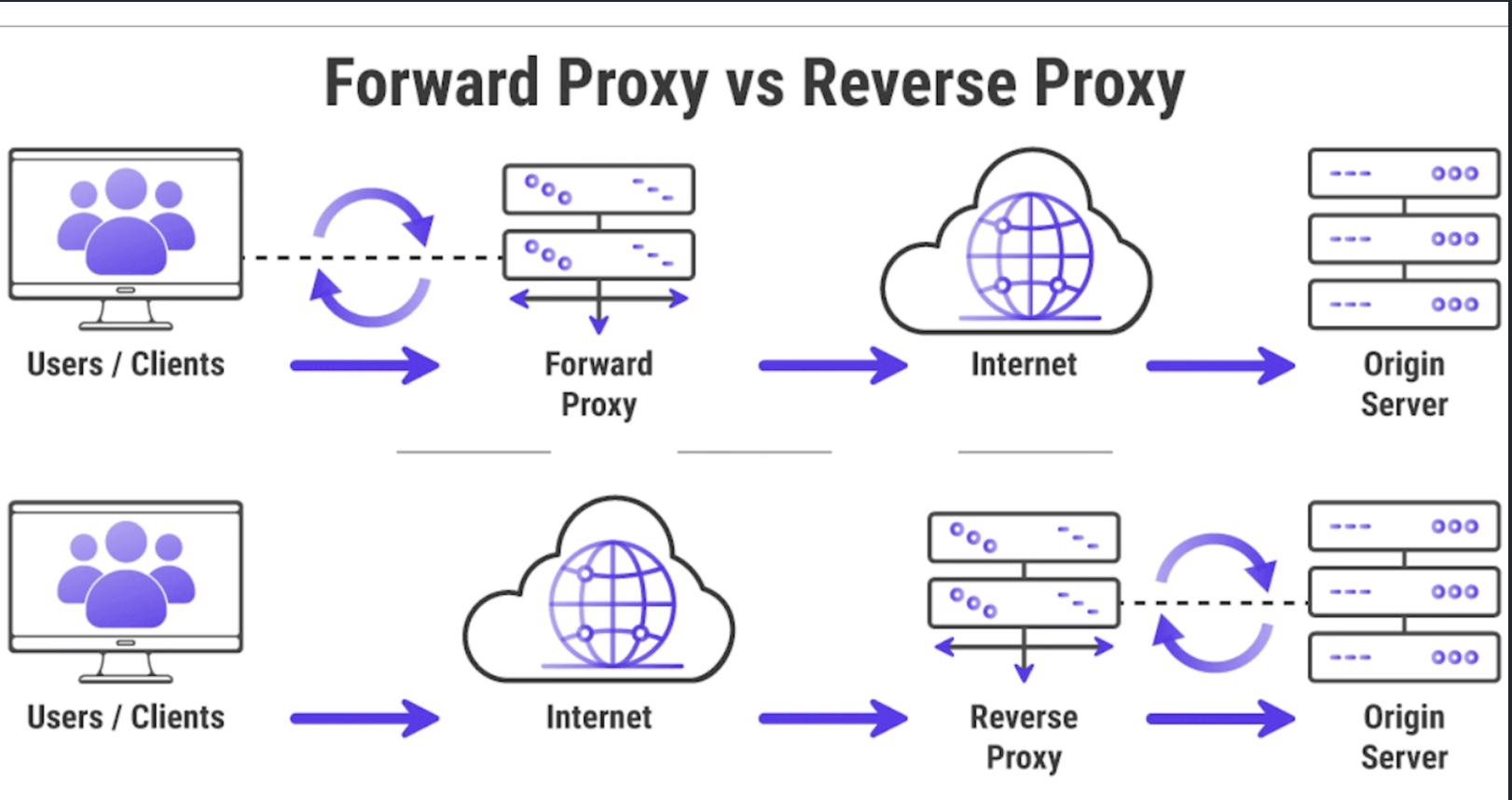
What is a Forward Proxy?
A Forward Proxy acts as a middleman between a client and the internet.
How it works:
- Sits between clients and the public internet.
- Client-facing: It primarily serves the client by forwarding requests to a server.
Use Cases:
- Access Control: Block access to certain websites or restrict internet usage within a company.
- Security: Scan for viruses and block harmful content.
- Monitoring: Log users’ web activity (e.g., employee monitoring).
- Content Filtering
- Caching
- Identity Protection
What is a Reverse Proxy?
A Reverse Proxy sits on the server side and handles requests from clients.
How it works:
- Acts as an intermediary for client requests.
- Primarily serves web servers, sitting in front of one or more.
- Forwards incoming client requests to the appropriate server(s).
Common Tools:
nginxas a reverse proxy.
Use Case:
- Load balancing across multiple backend servers.
- SSL termination (offloading SSL handshake from app servers).
What is a Transparent Proxy?
A Transparent Proxy intercepts network traffic between a user’s device and the internet without modifying requests or responses.
Characteristics:
- Also called inline, intercepting, or forced proxy.
- No need for users to configure anything—invisible to end-users.
Use Cases:
- Content filtering
- Traffic monitoring
- DDoS protection
- Authentication
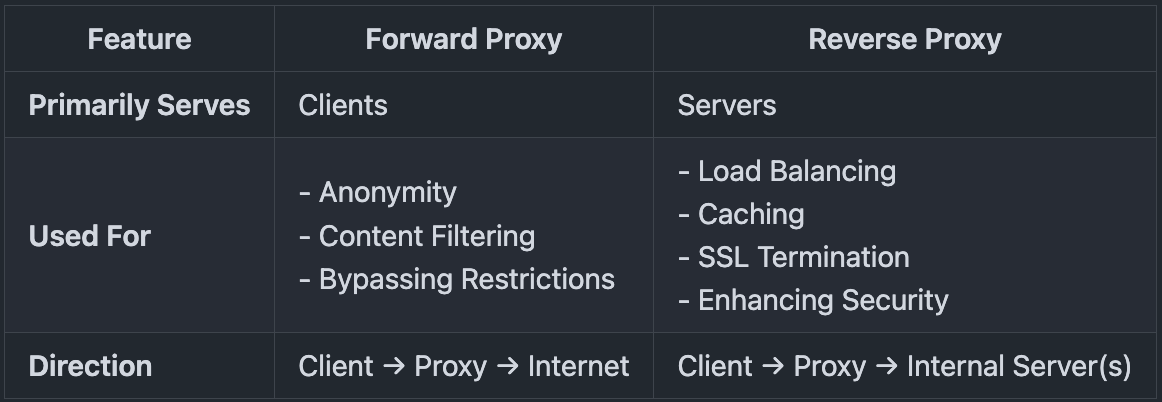
Forward Proxy vs Reverse Proxy
Why Use a Proxy for Load Balancing?
Using a reverse proxy for load balancing provides more granular and flexible routing, especially at Layer 7 (Application Layer).
Features:
- Route traffic based on headers, cookies, request content, etc.
- SSL Termination support
- Offloads CPU-intensive tasks like TLS handshake from backend servers
Proxies vs VPN
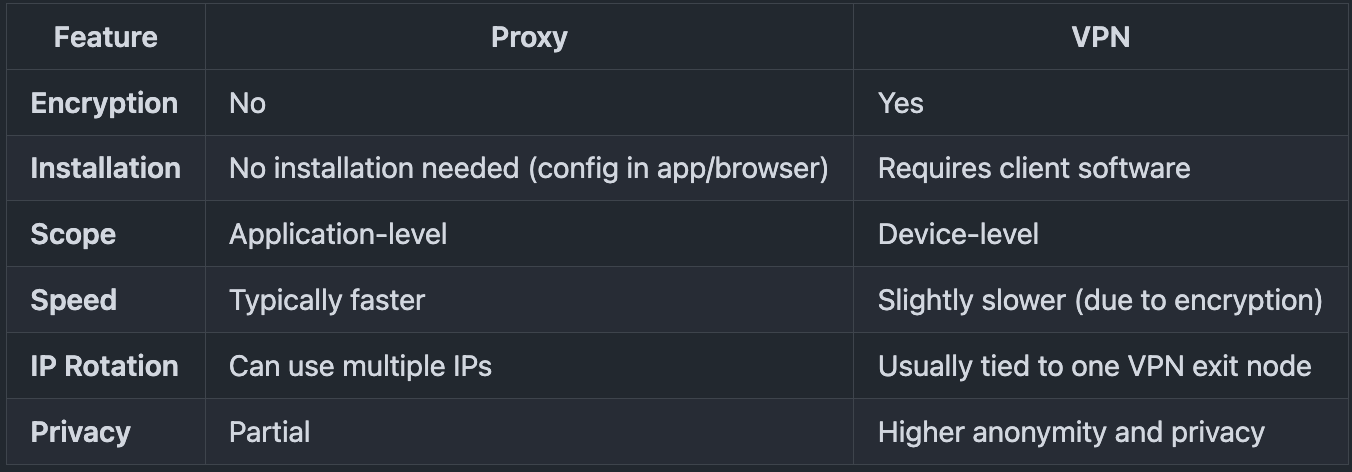
Note: A VPN is a specialized form of a forward proxy that includes encryption and operates at the system level.
Why Use Proxies in Data Collection?
When making a large number of requests to a server from a single IP, you're likely to get blocked. Proxies allow you to:
- Send traffic using multiple IPs to avoid detection.
- Distribute requests to avoid throttling.
- Scale data scraping or API consumption efficiently.
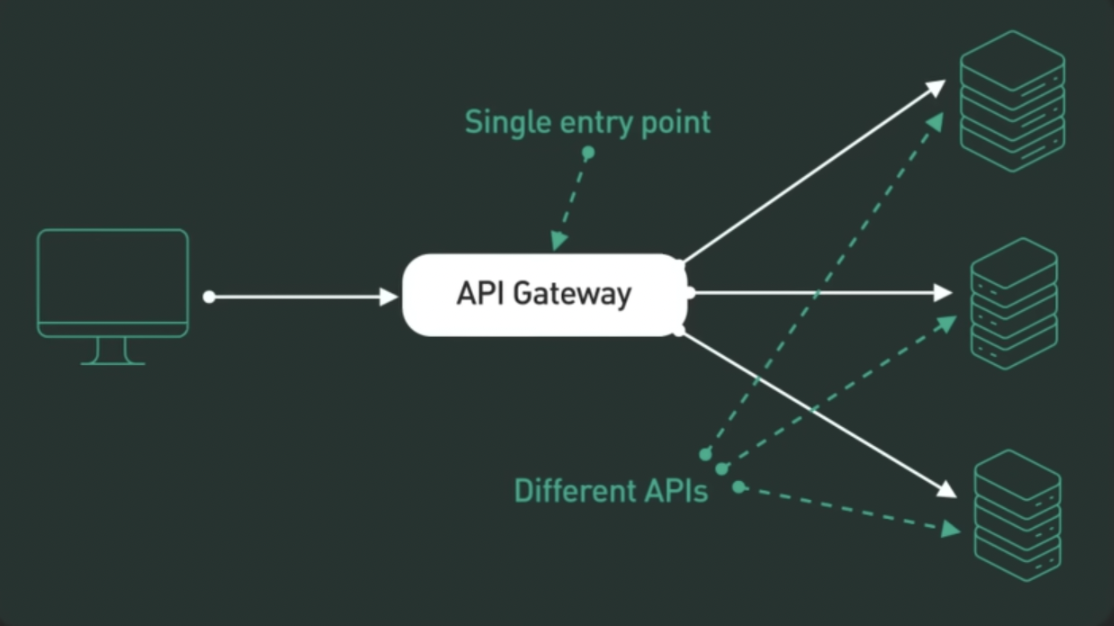
🔄 Quick Summary
- Forward Proxy: Used by clients to access the internet anonymously or securely.
- Reverse Proxy: Used by servers to manage incoming client traffic.
- Transparent Proxy: Invisible to clients, used for control and monitoring.
- VPN: Encrypted connection for full-device privacy and security.